
Everything you need to know about the Foreign Trade of India.
Foreign Trade (International Trade) is all about Exports and Imports.
What is the total value of India’s exports and imports? Which is higher – exports or imports?
What are the main export items? What are the main import items? What are the main export destinations? From which countries does India import the most? What is the trade balance? What is the Current Account Deficit? What is India’s Balance of Payment?
In this post, we explain the must-know concepts of International Trade in India in layman’s language.
Table of Contents
Subscribe to the ClearIAS YouTube Channel for more informative videos on UPSC preparation, tips, and strategies. Stay updated with our latest content and enhance your exam readiness.
👉 Which year are YOU targeting for success in the IAS/IPS/IFS Exam? 🚀
Business with foreign nations is not a new phenomenon in India. India is used to trade with foreign nations even in BC.
The Periplus of the Erythraean Sea is a document (written by an anonymous sailor from Alexandria about AD 100) describing trade between countries, including India.
Since 1498, Europeans have traded with the rulers of India using the sea route. The main export items then were spices like pepper, ginger, cinnamon, cardamom, nutmeg, mace, and cloves.
From 1947-1991, the Indian economy remained largely as a closed economy. High taxes were levied on the import of items. Foreign investments like FDI were restricted.
However, after the liberalization in 1991, foreign trade improved significantly.
Now, India exports around 7500 commodities to about 190 countries, and imports around 6000 commodities from 140 countries. Exports and Imports are not only restricted to commodities (merchandise). Service is also a major export/import item.
To make it simple, let’s summarise foreign trade of India as below:
Balance of Trade (BoT) is also known as Trade Balance.
Balance of Trade (Merchandise) = Export of goods – Import of goods
Balance of Trade (Services) = Export of services – Import of services
Note: In general, if someone mentions Balance of Trade, he/she is intending only the Balance of Trade (Merchandise)
India’s top five trading partners continue to be the USA, China, UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Hong Kong.
The composition of service exports has remained largely unchanged over the years.
Software services constitute the bulk of it at around 40-45 percent, followed by business services at about 18-20 percent, travel at 11-14 percent, and transportation at 9-11 percent.
Over the years, service imports in relation to GDP have been steadily rising putting pressure on BoP to worsen.
However, the increase in service imports to GDP ratio is inevitable given a rising level of FDI and a gradual upscaling of the Make in India program.
Business Services, Travel, and Transportation are the three top service imports.
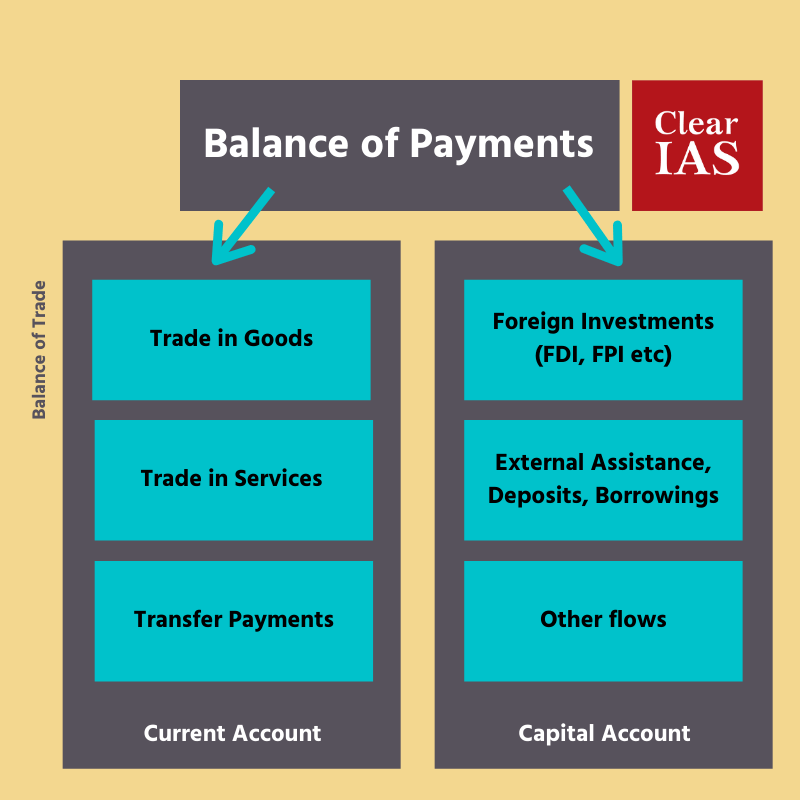
Balance of Payments (BoP) statistics systematically summarise, for a specific period, the economic transactions of an economy with the rest of the world.
The compilation and dissemination of BoP data is the prime responsibility of RBI.
BoP = net credit in ( Current Account + Capital Account and Financial Account).
India’s Balance of Payments (BoP) position witnessed great improvement since liberalization in 1991.
India’s foreign reserves stood at US$ 572 billion as on November 2020.
Foreign Exchange (Forex) Reserves include Foreign Currency Assets, Gold, Special Drawing Rights (SDRs), and Reserve Position in the IMF (Gold Tranche or Reserve Tranche).
Global Trade was growing at 5.7 percent in 2017. However, in 2019-20, it is estimated to grow only at 1.0 percent.
India now ranks 68 out of the 190 countries under the indicator “Trading across Borders” in the Ease of Doing Business Report published by the World Bank. (2019)
The logistics industry of India is currently estimated to be around US$ 160 billion and is expected to reach US$ 215 billion by 2020.
Net Remittances are part of the Current Account in the Balance of Payments statement published by RBI.
Net remittances from Indians employed overseas have been constantly increasing year after year.
FDI and FPI are showing a positive trend in recent years.
After witnessing a significant decline from 2014-15, India’s external liabilities (debt and equity) to GDP increased at the end of June 2019 primarily driven by an increase in FDI, portfolio flows, and external commercial borrowings (ECBs).
External debt as of the end of September 2019 remains low at 20.1 percent of GDP.
The Foreign Trade Policy, 2015-20, notified by the Central Government, is an exercise of powers conferred under Section 5 of the Foreign Trade (Development & Regulation) Act, 1992 OR FT (D&R) Act.
Export trade is regulated by the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) and its regional offices, functioning under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Department of Commerce, Government of India.
Policies and procedures required to be followed for exports from India are announced by the DGFT, from time to time.
[Question UPSC CSE 2020] With reference to the international trade of India at present, which of the following statements is/are correct?
1) India’s merchandise exports are less than its merchandise imports.
2) India’s imports of iron and steel, chemicals, fertilizers, and machinery have decreased in recent years,
3) India’s exports of services are more than its imports of services.
4) India suffers from an overall trade/current account deficit.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 3 and 4 only
Answer: (d) 1, 3 and 4 only
Learning Zone: The merchandise trade deficit is the largest component of India’s Current Account Deficit (CAD). As per RBI’s data, India’s merchandise exports are higher than that of imports. Hence statement 1 is correct
Commodity-wise composition of imports shows that imports of iron and steel, organic chemicals, and industrial machinery have registered positive growth rates as % of share imports. Hence statement 2 is incorrect.
As you learned in this article, India’s net services (service exports – service imports) have been in surplus. Hence statement 3 is correct.
Trade Deficit is usually taken as the difference between the exports of goods minus the import of goods. Current Account Deficit (CAD) denotes the net export of goods, services, and transfer payments. India has both a Balance of Trade Deficit as well as a Current Account Deficit (CAD). Hence statement 4 is correct. Therefore, the correct answer is (d) 1, 3, and 4 only.